Discrete Fluids
Copyright: Caltech Applied Geometry Lab - Publications
Abstract:
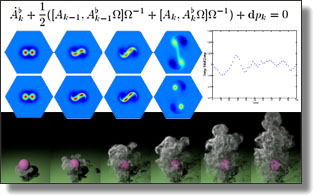
The geometric nature of Euler fluids has been clearly identified and extensively studied over the years, culminating with Lagrangian and Hamiltonian descriptions of fluid dynamics where the configuration space is defined as the volume-preserving diffeomorphisms, and Kelvin's circulation theorem is viewed as a consequence of Noether's theorem associated with the particle relabeling symmetry of fluid mechanics. However computational approaches to fluid mechanics have been largely derived from a numerical-analytic point of view, and are rarely designed with structure preservation in mind, and often suffer from spurious numerical artifacts such as energy and circulation drift. In contrast, this paper geometrically derives discrete equations of motion for fluid dynamics from first principles in a purely Eulerian form. Our approach approximates the group of volume-preserving diffeomorphisms using a finite dimensional Lie group, and associated discrete Euler equations are derived from a variational principle with non-holonomic constraints. The resulting discrete equations of motion yield a structure-preserving time integrator with good long-term energy behavior and for which an exact discrete Kelvin's circulation theorem holds.
| Projects Page | DCM People | DCM Projects |

 |
 |